What is SPO2 or Oxygen Saturation?
What is SPO2?
SpO2, also known as Blood Oxygen Saturation, an estimate of the amount of oxygen in the blood. Which refers to the amount of oxygenated hemoglobin in the blood. Hemoglobin is a protein in red blood cells that transports oxygen and carbon dioxide. It is found inside red blood cells and gives them their red color.
Understanding SpO2 and Normal Oxygen Levels
A measurement of your blood oxygen is called your oxygen saturation level. Your blood oxygen level is a measure of how much oxygen your red blood cells are carrying. Your body closely regulates your blood oxygen level. It is vital to your health to maintain the precise balance of oxygen-saturated blood.
A SpO2 reading of 95% or greater is generally considered to be a normal oxygen level. However, a SpO2 reading of 92% or less (at sea level) suggests that your blood is poorly saturated. Insufficient saturation can cause a range of adverse health conditions including chest pain, shortness of breath, and increased heart rate.
Measuring SpO2
There are two ways that the blood can be tested to ensure it contains normal oxygen levels.
- An arterial blood gas (ABG) test is a blood test and it’s called Arterial blood gas. It also can detect the level of other gases in your blood, as well as the pH (acid/base level). An ABG is very accurate, but it’s invasive.
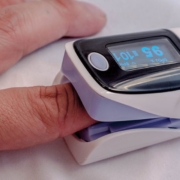
- The most common way is to use a pulse-oximeter to measure the SpO2 levels in the blood. Pulse oximeters are relatively easy to use, are very accurate despite their low price point.
A measurement of your blood oxygen is called your oxygen saturation level. Good blood oxygenation is necessary to supply the energy your muscles need in order to function, which increases during activity. If your blood oxygen level is below-normal it is called hypoxemia and that could be a sign of poor blood oxygenation, also called hypoxia. Your doctor can provide recommendations as to what ranges of oxygen levels are acceptable for you.
Disclaimer
The information, including but not limited to, text, graphics, images and other material contained on this website are for informational purposes only. The purpose of this website is to promote broad consumer understanding and knowledge of various health topics. It is not intended to be a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the advice of your physician or another qualified healthcare provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition or treatment and before undertaking a new health care regimen, and never disregard professional medical advice or delay in seeking it because of something you have read on this website.